CT scan vs. MRI. Do you know the difference?
CT scans and MRI are two different medical imaging methods that create detailed images of internal body parts of the human.
These can include joints, bones, and different organs.
Moreover, doctors can offer CT scans or MRI scans that will help to diagnose a wide range of medication conditions.
Both of these scans have similar uses. However, they produce images in different ways.
A CT scan tends to use X-rays, while an MRI scan uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves.
It is important to note that CT scans are more and less expensive.
However, an MRI scan can produce more detailed images.
Keep on reading to learn more about CT scans vs. MRI, their uses, procedures, and safety.
CT Scan vs. MRI
CT scan vs. MRI is two different ways of creating detailed images of the internal parts of the patient.
Doctors can then analyze the images to detect any abnormality like fractures in bones, tumors in organs, or joint damage.
It is important to note that in some cases, your doctor may prefer CT scans to a CAT scan, which stands for computerized axial tomography.
During a CT scan, the patient will need to lie down in a large X-ray machine: a CT scanner.
The scanner then sends images to the computer.

On the other hand, MRI stands for magnetic resonance imagery. This type of scan uses radio waves and magnets to create images.
During an MRI scan, the patients will have to lie down in the MRIC scan, which uses radio waves to bounce off water molecules and fat cells in the body.
The scanner also sends images to the computer.
Moreover, CT scans tend to be more common than MMRI
However, CT scans vs. MRI, MRI scans tend to produce better images than a CT scan.
CT Scan vs. MRI: Uses
One of the important things to note about CT scans vs. MRI, magnetic resonance imaging is they are very similar.
CT scans tend to be more common as they are less expensive and still provide good detail.
The doctor may order an MRI scan when they need to create more accurate detailed images of the body.
Moreover, common uses of a CT scan include examining and looking for:
However, doctors commonly use MRI scans to diagnose issues with bones, organs, and joints, including those that affect the:
- ankles
- breasts
- brain
- heart
- joints
- wrists
- blood vessels
Are they Safe?
While considering CT scan vs. MRI, it is important to note that both procedures are safe.
They may, however, pose slight risks, which differ between the types of scans.
During a CT scan, the patient may receive a very small dose of radiation, however, doctors often do not consider it harmful.
Moreover, CT scans use ionizing radiation which has the potential trail to affect biological tissues.
According to the National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering, the risk of developing cancer from exposure to radiation is generally small.
It is important to note that CT scans and X-rays may not be safe during pregnancy, so doctors may not recommend MRI scans or ultrasound scans instead.
However, the patient may still need to avoid using MRI scans, especially during the first trimester, as a precaution.
Furthermore, MRI scans do not use radiation.
They do, however, use strong magnetic fields.
Patients must let the technician know if they have any form of a medical implant, like a pacemaker, insulin pump, or cochlear implant.
MRI scans produce loud sounds, so patients may want to wear earplugs or headphones to dull the noise.
In case the patient is claustrophobic they may find MRI scanners difficult to tolerate.
Although several types of open MRI scanners now exist to get around this problem.
For both, CT scans vs. MRI a doctor can also recommend using a contrast dye to make the images clearer.
Some patients, however, may react badly to a certain type of dye.
CT scan with a Contrast
CT scans can provide detailed images of bones, tissues, and even blood vessels in the body of the patient.
However, the images the scan prodcues appear in shades of blacks and greys.
It can be difficult at times even for a trained eye to differentiate one tissue type from another in certain circumstances.
Moreover, contrast dyes contain barium or iodine and can also give in a number of ways. including orally and intravenously, in your vein.
These dyes tend to increase the contrast dye and resolution of the final images th scan prodcues for the most exact diagnosis.
However, there are a few risks associated with using contrast dye.
For instance, there is a high chance of allergic reactions to the dyes, and they are also not good for the kidneys of the patient.
Still, every CT scan exposes the patient to a certain level of radiation and a CT scan with contrast may produce better results than one without it.
Furthermore, it may also prevent the need for repeated scans.
Below, you can see the com
| With contrast | Without contrast |
|---|---|
| acute appendicitis | acute stroke |
| staging cancer | closed head injuries |
| diverticulitis | lung disease |
| inflammatory bowel disease | tissue swelling or injury in your arms or legs |
| pancreatitis | kidney stones |
| pulmonary embolism | spinal trauma |
CT scan Procedure
CT scan is a painless procedure, however, it does take a few steps to get images.
Preparing for a CT scan
A patient does not have to prepare much for a CT scan. The patient may or may not need contrast dye.
However, they may need a contrast dye in case the doctor needs to diagnose traumatic injuries or a stroke.
In case a doctor schedules a patient for contrast dye, they may need to refrain from eating solid foods for up to 4 hours before the test.
This is especially true in case the doctor needs images of the abdomen of the patient.
During the Scan
When the patient arrives for the scan, they will need to change into the hospital gown.
The technician during the scan may insert an IV catheter in the arm or leg or ask whether the patient has removed any metal devices or medication patches.
When it is time to begin th scan, the technician will position the patient on a long narrow table and secure them with velcro straps or other safety devices.

Then the table will slide in and out of the circular scanner depending on the part of the body the doctors want to visualize.
The technician will leave the room before operating the scanner and give the patient instructions over an intercom.
CT scan machine will rotate around the patient making a loud noise while they may also need to hold their breath or maintain a certain position.
After the Scan
Once the scan is over, the images are sent to the radiologists for examination.
A radiologist is a doctor who specializes in diagnosing and treating conditions using imaging techniques like CT scans or X-rays.
Furthermore, the doctor will follow up with the patient to explain the results.
MRI Scan Procedure
MRI scans produce highly detailed images.
Preparation
In the case of an MRI scan, the patient will need little to no preparation.
On arrival at the hospital, the patient will need to change into a gown.
As the MRI machines use powerful magnets, it is important to avoid or have no metal objects present in the scanner.
Moreover, the doctor will ask the patient to remove any metal jewelry or accessories that may interfere with the machine.
In some cases, the patient may receive an injection of intravenous IV contrast liquid to improve the visibility of a particular tissue that is relevant to the scan.
Once the patient enters the scanning room, the doctor will help them onto the table to lie down and the staff will make sure there they are as comfortable as possible.
During the Scan
Once in the scanner, the MRI technician will communicate via intercom to make sure that the patient is comfortable.
However, they will not start until the patient is ready.
During the scan, it is important to stay still as any movement can disrupt the x-ray images.
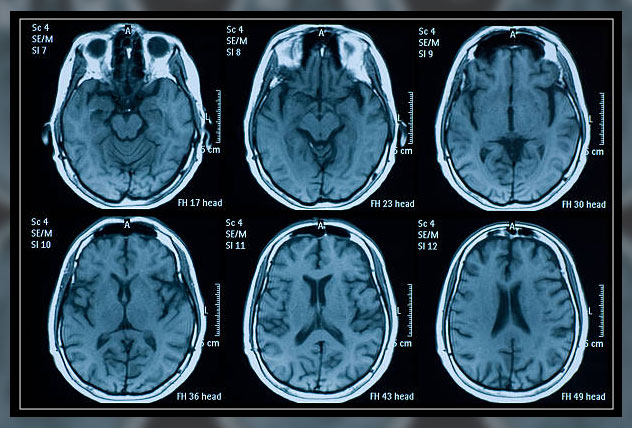
Loud clanging voices will come from the scanner, which is perfectly normal.
Depending on the images, at times, it is important for the patient to hold their breath.
In case the patient is uncomfortable, they can speak to the MRI technician via intercom and request to stop the scan.
After the MRI Scan
After the scan, the radiologist will examine the images to check whether they need any more.
If the radiologist is satisfied, the patient can go home.
While the doctor will schedule an appointment with the patient to discuss the results.
Choosing the Right Scan
While choosing CT scan vs. MRI, the uses are very similar.
The doctor will decide which scan is right based on a range of factors. These include:
- the medical reason for the scan
- the level of detail that is necessary for the images
- whether the woman is pregnant or not
- whether a person has claustrophobia or other factors that may make MRI scans difficult for them to tolerate.

Choosing CT scans vs. MRI scans, MRIs tend to produce a more detailed image of soft tissue, ligaments, or organs.
However, problems that may be easier to see with an MRI scan include soft tissue damage, torn ligaments, and herniated disks.
Doctors can use a CT scan for creating a generalized image of the body part or for getting images of the organ or head fractures.
Final Thoughts
CT scans vs. MRI are two methods for imaging internal body parts. Moreover, they have similar uses, however, produce pictures in different ways. CT scans use X-rays, while MRIs use strong magnets and radio waves.
A CT scan is often good for larger areas while an MRI scan prodcues a better overall image of the tissue under examination. Both have, however, risks, but are relatively safe procedures. A doctor will suggest which scan is right for the patient, depending on the range of factors.