
In a dental setup, you will need a steam sterilizer machine to reuse your equipment without the spread of disease and infection.
While some instruments are primarily disposable, many are also reusable.
Therefore, to reuse them, you will need to first sterilize them in an autoclave.
Their use is popular in healthcare and industrial applications.
This article discusses how you can use the machine to sterilize your equipment and instruments in a dental setting.
Keep reading below to know more.
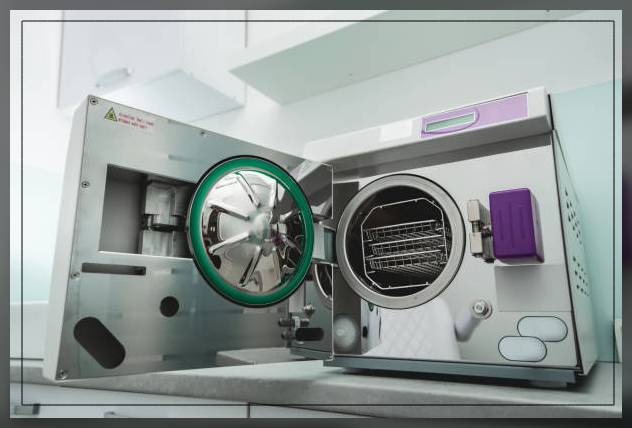

What is a Steam Sterilizer Machine?
An autoclave is the other name for a steam sterilizer.
As the name suggests, this method of sterilization uses moist heat as saturated steam under pressure.
This is the most dependable and common method for sterilization.
The machines use the steam under pressure to kill the harmful bacteria, fungi, viruses and spores present on the item that is inside the pressure vessel.
The items inside are heated to an appropriate temperature for a certain exposure time.
The moisture in the steam destroys the protein structure of the bacteria and spores thereby sterilizing the equipment.
There are 4 parameters for steam sterilization:
- temperature
- steam
- time
- pressure
In order to obtain the microbicidal activity, there should be a specific temperature.
The common temperatures are around 121 degrees Celcius and 132 degrees Celcius.
This temperature remains at a minimum temperature to kill the microorganisms.
This makes the ideal steam which is usually entrained water and dry saturated steam.
The minimum exposure period for sterilization is usually 30 minutes at 121 degrees Celcius in a gravity displacement sterilizer.
For a pre-vacuum sterilizer it will be 4 minutes at 132 degrees Celcius.
However, the time can vary depending on whether the item is wrapped it unwrapped, also depending on the type of the equipment and the sterilizer.
The pressure of the machine allows it to reach high temperatures quickly that will kill the microorganisms.
The first form of the autoclave was a steam digester.
Physicist Denis Papin holds the credit to invent it in 1679.
However, the steam sterilizer as we know it today did not come into being till 1879 by French microbiologist Charles Chamberland.
Later the disinfecting and sterilization began in 1881 by Robert Koch.
He highlighted the power of moist steam to penetrate and kill microbes in comparison to dry heat.

Types of Machines
The two main steam sterilizers are high-speed pre-vacuum sterilizers and gravity displacement autoclaves.
There is not a huge difference in the workings of the two sterilizers.
In fact, the pre vacuumed sterilizer is similar in many ways except that it has a vacuum pump to ensure air removal before the steam admits into the sterilizing chamber.
Due to the vacuum pump, there is instantaneous steam penetration in the porous loads.
In this sterilizer, the Bowie-Dick test checks for air leaks and improper air removal daily before the first processed load.
It contains folded preconditioned 100 percent cent surgical towels.
The test sheet is in the center of the pack.
The test pack is placed at the bottom of the sterilizer rack, over the drain, near the door, horizontally in front and in an empty chamber that is run for 134 degrees Celcius for 3.5 minutes.
The air that does not leave the chamber interferes with the steam contact thus, producing a spot on the test sheet.

For the gravity displacement autoclave, they process the nonporous articles, water, laboratory media waste and pharmaceutical products that have surfaces with direct contact with steam.
Steam is lighter than air.
Hence, this sterilizer uses a mechanism whereby steam admits from the top or sides of the chamber and pushes air out from the bottom of the sterilizing chamber via the drain vent.
However, there may be incomplete air elimination.
Therefore, the penetration time into porous items in longer.
For instance, microbiological waste requires 45 minutes at 121 degrees Celcius.
Besides these two, there is the steam flush pressure pulsing process.
It removes air by using a steam flush and a pressure pulse alternatively.
Though, it is different because air leaks do not impact the effectiveness of the process as steam is above atmospheric pressure.

Steam Sterilization Process
So now you know that the basics of steam sterilization are exposing the medical items to saturated steam under pressure.
Steam increases the ability to kill the microorganisms by reducing the temperature and time that denatures proteins in the microorganisms.
To achieve that, a sterilizer machine goes through three phases.
Phase 1: Conditioning
Right at the beginning of the procedure, the machine needs to remove air.
This is because the air interrupts sterilization.
Thus, in conditioning, the air removes the sterilizer.
In a pressured vacuum system also known as the dynamic air removal system.
Though, it can also remove using steam flushes and pressure pulses.
In gravity displacement sterilizers, the steam displaces the air down through the drain vent.
Next, the load is heated to the recommended temperature settings for the sterilization process.
Phase 2: Exposure
Once the chamber and load reach the temperature, then it is time to expose the items to the steam.
The sterilizer drain closes while steam admits into the chamber, increasing the temperature and pressure of the sterilizer.
These medical and lab equipment are exposed to steam at a set temperature and time.
The time and temperature settings are set according to the guidelines of the machine and the equipment.
Phase 3: Exhaust
Once the sterilization is done, the machine removes the steam as the last step of the process.
The steam removes from the sterilization drain releasing the pressure inside the chamber.
It is also the cool-down or drying phase, as the removal of the pressure allows the items to dry down.
A vacuum removes the steam and also dries down the load.
The steam composition, system maintenance, construction, a utility supply and sterilizer performance are crucial to the system.
The steam should be 97 percent vapor and 3 percent water.

Components of a Steam Sterilizer Machine
Vessel
The main body is the vessel.
It has an inner chamber and an outer jacket.
The jacket is filled with steam to reduce condensation in the chamber and the overall time for sterilization.
You should choose a vessel with a full jacket because of temperature uniformity, minimizing wet steam and the likelihood of wet packs.
Vessela varies from 100L to 3000L in size.
Plus they use stainless steel and nickel-clad 316L inner chamber while outer chambers are 316L carbon-clad.
Safety Valve
Since there is elevated pressure in an autoclave, it is crucial to have many safety valves and features throughout so there is no danger to the users.
The safety valve is the final fail-safe device in case all other electronic controls fail.
Hence, you should regularly inspect it if it works properly.
Control System
In order to operate the machine, it contains a control system.
All autoclaves need it because the sterilization works at a set temperature and time.
The valves along with other components, open and close in a sequence.
Hence, it needs a simple push-button microprocessor or a complex programmable logic controller.
Waste-Water cooling Mechanism
Before the effluent, air and steam enter the draining pipe, they first cool off in the wastewater mechanism.
Municipalities do not allow effluent to be over 140 degrees Fahrenheit which can potentially damage the pipes.
Hence, it needs cooling before it leaves the sterilizer.
Cold tap water quality can help cool it off and autoclaves have a built-in system to reduce excess water usage.
Thermostatic Trap
A thermostatic trap allows water and air to escape the chamber.
They remove condensate which is water while also preventing the way of the dry steam.
These are usually temperature-sensitive valves that close when heated beyond a certain point.
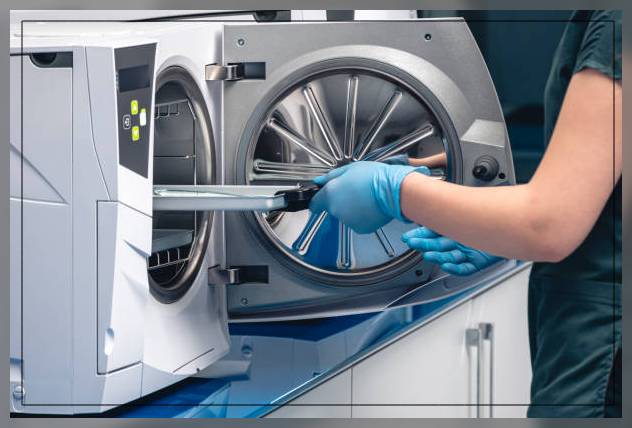

Other Components
Steam Generator and a Vacuum System
If the sterilizer uses a steam source then it contains a central house boiler.
Though, if that is insufficient then you will need an electric steam generator which is a separate boiler.
It sits under the chamber and uses electrical heating to heat the steam.
A vacuum system removes all the air in the chamber.
It enables to use of the vacuum before the beginning of a cycle and as it ends.
This removes any remaining steam in the chamber and also dries out the items.
Both the steam generator and the vacuum system are optional components that are not present in all sterilizers.
Time and Temperature
Other than its components, it is quite important to ensure the right steam sterilization temperature and time.
The moist heat sterilization temperature range for autoclave sterilization is either 121 degrees Celcius (250° F), 132 degrees Celcius (270°F) or 135 degrees Celcius (275°F).
This autoclave temperature will allow to the killing of the microorganisms for the minimum time recommended.
The time is dependent on the temperature to create a total exposure phase.
It varies with the material composition of the lab sterilization equipment as well as its size, shape, density and weight.
Finally,
Medical steam sterilizer machine comes in use for sterilizing implanted medical devices, surgical instruments, surgical linens and drapes.
This ensures that there is no infection transmission in your medical practice protecting both patients and the healthcare workers from disease and infection.
If you are looking to buy a steam sterilizer machine or direct steam injection system, look into our shop to discover various state-of-the-art machines with modern technology.



Comments