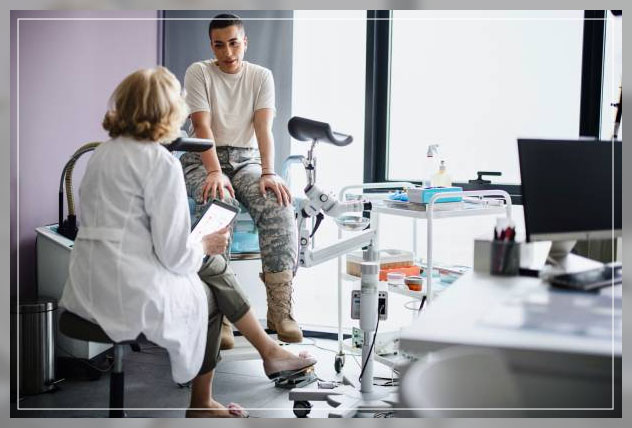
A Pap Smear Test is a procedure that helps to diagnose and test for cervical cancer in women.
A pap smear is also called a Pap Test. This test involves collecting cells from the cervix of women which is the lower, narrower end of the uterus.
It is at the top of the vagina of a woman. Detecting cervical cancer early with a pap smear test gives a person a greater chance of curing it.
Moreover, with the help of this test, the doctor can also detect changes in the cervical cells that suggest that cancer may develop in the future.
Detecting such abnormal cells early is the first step in halting the possible development of cervical cancer.
Keep on reading.
Pap Smear Test
A pap smear or a pap test is a screening procedure for cervical cancer.
It helps to test for the presence of precancerous or cancerous cells on the cervix of a woman.
A cervix is the opening of the uterus.

During this procedure, the doctor will gently scrape away and examine cells from the cervix for abnormal growth.
Moreover, the doctor will perform the procedure and pelvic exam at their office.
It may be mildly uncomfortable, however, it does not cause any long-term pain.
Learn more about CRP Test: What is it, Procedure, and More here.
Uses of Pap Smear Test
The American Cancer Society recommends that screening should take place or begin at the age of 25 or age 30.
Some women may be at an increased risk for cancer or infection, and they may need more frequent tests if:
- a person is HIV positive
- have a weakened immune system from chemotherapy or an organ transplant.
Therefore, if a woman is over 25 and does not have an abnormal Pap test, they should ask there doctor about having one every five years.
This is often the case when they have to combine the test with human papillomavirus, HPR screening.
Moreover, current guidelines recommend that people between the ages of 25 and 65 should have an HPV test every five years.
HPV is a virus that causes warts and also increases the chance of cervical cancer.
It is important to note that HPV types 16 and 18 are the primary causes of cervical cancer.
Thus, if a person has HPV, they may be at an increased risk of developing cervical cancer.
Women over the age of 65 with a history of normal pap smear tests may be able to stop having the test in the future.
A person should still get this test depending on the age, regardless of the sexual activity status.
This is because the HPV virus can be dormant for years and then suddenly become active.
Learn more about Blood Test: All You Need to Know here.
How often do Women need Pap Smear Tests?
How often one needs a Pap smear test is determined by various factors, including the age and risk of a person.
| Age | Pap smear frequency |
| < age 21 years old, | none needed |
| 21-29 | every 3 years |
| age 30-65 | every 3 years or an HPV test every 5 years or a Pap test and HPV test together every 5 years |
| 65 and older | a person may no longer need Pap smear tests; talk to the doctor to determine the specific needs |
However, these recommendations only apply to women who have a cervix, according to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists
Women who undergo hysterectomy with removal of the cervix and have no history of cervical cancer do not need this screening.
It is important to note that recommendations tend to vary and are often individualized for women with compromised immune systems.
Or those with a history of precancerous or cancerous lesions.
Preparing for a Pap Smaer Test
A person should schedule a pap smear test with the annual gynecological examination or request a separate appointment with the gynecologist.
It is important to note that most insurance plans cover pap smear tests, so the patient will not need to pay a co-pay.
However, if a woman is menstruating on the day of the test, the doctor may want to reschedule the test.
This is because the result in such cases can be less accurate.
Moreover, it is important to note that a woman should avoid having sexual intercourse, douching, or using spermicidal products the day before the test.
This is due to the fact that such things can interfere with the results as well.
In most cases, it is safe to have Pap Smear test in the first 24 weeks of the pregnancy.
After the test, the test can be more painful. Moreover, a woman should also make sure to way until 12 weeks after giving birth to increase the accuracy of the results.
As pap smears go more smoothly when the body of a person is relaxed, it is important to stay calm and take deep breaths during the procedure.
Learn more about Pregnancy Test: Blood Test, Kits, Ultrasound, And More here.
Pap Smear Procedure
It is important to note that pap smear tests can be slightly uncomfortable, however, the test is very quick.
During the procedure, the woman will lie on her back on an examination table with the legs spread and feet resting in supports: stirrups.
The doctor will slowly insert a device called a speculum into the vagina.
This device will help to keep the vaginal walls open and also provides access to the cervix.
Then the doctor will scrape a small sample of cells from the cervix.
Moreover, there are a few ways a doctor can take this sample. These include:
- some use a tool called a spatula
- some can use a spatula and a brush
- while others will use a device: cytobrush which tends to be a combination of spatula and brush
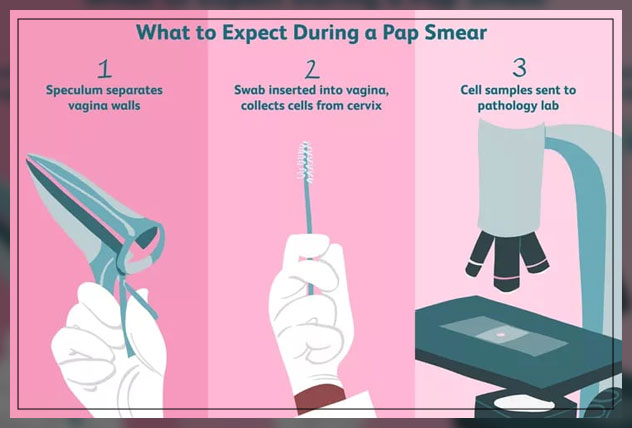
Most women tend to feel a light push and irritation during this brief scraping.
The doctor will preserve the samples of cells from the cervix of the women and then send them to the lab to test for the presence of abnormal cells.
After the test, a person may feel mild discomfort from the scraping or a bit of cramping.
Furthermore, they could also experience very light vaginal bleeding immediately following the test.
Therefore, it is important for the person to inform or tell the doctor if discomfort or bleeding continues after the day of the test.
Interpreting the Results
There are two possible results from a Pap Test: normal or abnormal.
Let’s discuss them as follows:
Normal Pap Smear
In the case the results are normal then this means that there is no identification of abnormal cells.
Normal results, in some cases, are also referred to as negative.
However, if the pap test results are normal, the person will not need a Pap smear for another three years.
Abnormal Pap Smear
If the tests are abnormal, this does not mean that the person has cancer.
I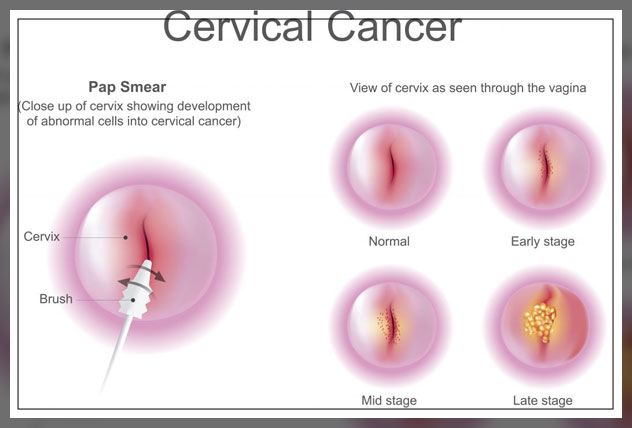 t simply means that there are abnormal cells on the cervix, some of which can be precancerous.
t simply means that there are abnormal cells on the cervix, some of which can be precancerous.
There are different levels of abnormal cells:
- atypia
- mild
- moderate
- severe dysplasia
- carcinoma in situ
Milder abnormal cells tend to be more common than severe abnormalities.
Moreover, depending on what the test results show, the doctor can further recommend an increase in the frequency of pap smears and getting a closer look at the cervical tissue with a procedure: colposcopy.
During a colposcopy exam, the doctor will use light and magnification to see vagina and cervical tissues more clearly.
In some cases, however, they may also take a sample of the cervical tissue in a procedure: biopsy.
How Accurate are the Results?
It is important to note that pap smears are very accurate.
Regular pap screenings tend to reduce cervical cancer rates and mortality by at least 80%.
Though it can be uncomfortable, the brief discomfort can help protect the health of a person.
Does Pap smear test for HPV
The main goal of a pap smear is to identify cellular changes in the cervix, which can occur due to HOV.
By detecting cervical cancer cells early with a pap smear, treatment can begin before it spreads and becomes a larger concern.
Moreover, it is also possible to test for HPV with a pap smear specimen as well.
The person can contract HPV from having sex with men or women.
In order to lower the risk of contracting the virus, one should practice sex with a condom or other barrier methods.
All sexually active women tend to be at risk of contracting HPV and should get a pap smear at least every three years.
However, this test will not help detect other sexually transmitted infections, STIs.
It can occasionally detect cell growth that shows other cancers, but one should not rely on it for that purpose.
The course of Action in case of Abnormal Results
In case of abnormal results, the next course of action may be:
Atypical Squamous Cells of Undetermined Significance, ASCUS
Squamous cells are thin and flat and tend to grow on the surface f a healthy cervix.
In the case of ASCUS, the pap smear will show slightly abnormal squamous cells, however, the changes do not clearly suggest the presence of cancerous cells
Moreover, with a liquid-based test, the doctor will reanalyze the sample to check for the presence of viruses that could promote the development of cancer like types of human papillomavirus HPV.
If no risk viruses are present, the abnormal cells found as a result are not of great concern.
However, if worrisome viruses are present, a person will need further testing.
Squamous Intraepithelial Lesion
This term is to indicate that the cells from the pap smear may be precancerous.
However, if the changes are low grade, it means that the size, shape, and other characteristics of the cells suggest that if a precancerous lesion is there, it is likely to be years away from becoming cancer.

But if the changes are high grade, there is a greater chance that the lesion may develop into cancer sooner than later and additional diagnostic testing is necessary.
Atypical Glandular Cells
Glandular cells tend to produce mucus and grow in the opening of the cervix and within the uterus.
Moreover, atypical glandular cells may appear to be slightly abnormal, however, it is unclear whether they are cancerous or not.
Further testing can help to find the source of abnormal cells and their significance.
Squamous Cell Cancer or Adenocarcinoma Cells
This result means that the cells appear to be abnormal that the pathologist is almost certain a cancer is present.
Squamous cell cancer refers to cancers arising in the flat surface cells of the vagina or cervix.
While Adenocarcinamo refers to cancers arising in glandular cells.
Furthermore, if such cells are present, the doctor will recommend a prompt evaluation.