If you are running a dental office, then dental digital radiography will be a part of your practice.
Yes, good oral and dental hygiene can protect the life of your patients and many researchers now believe that there is a link between tooth loss and risk of heart disease.
Considering that heart diseases are the leading causes of death around the world, making sure that your patients receive good dnetal services should be your priority.
Moreover, the first step in making sure this is to get dental digital radiography procedures like dental x-rays at your office.
Oral images can help you and your dental hygienist to diagnose issues that can lead to tooth decay, or worse, tooth loss.
There are different types of dental digital radiography techniques.
Learning about their advantages, types, and disadvantages can help you get the right machines in your dnetal setting.
How? Keep on reading.
Dental Digital Radiography
Today dental professionals are using digital radiography to help better detect, diagnose, treat, and monitor oral conditions and diseases.
Moreover, digital radiography is a type of X-ray imaging that uses digital x-ray reasons to replace traditional photographic x-ray film.
It helps to produce enhanced images of teeth, gums, and other oral structures and conditions.
These are helpful in a number of ways for dental professionals.
Furthermore, dental digital images that you can get are through three methods:
- direct method
- indirect method
- semi-indirect method
The direct method uses an electric season that you will have to place in the mouth. It uses an electric session to record images.
The indirect method uses an X-ray film scanner to view traditional dental x-rays just like digital images.
While the semi-indirect method combines both sensor and scanner to convert dental x-rays into digital film.
Thus you can use CMOS APS for this purpose.
Learn more about Dentist Equipment List here.
Uses of Dental Digital Radiography
You can take dental digital radiography either inside, i.e. intraoral, or outside, i.e. extraoral of the patient.
Intraoral X-rays are the most common types of dental digital radiography methods.
Moreover, these provide great detail and can help to detect cavities.
These can also help detect:
- the status of developing teeth
- monitor teeth and bone health
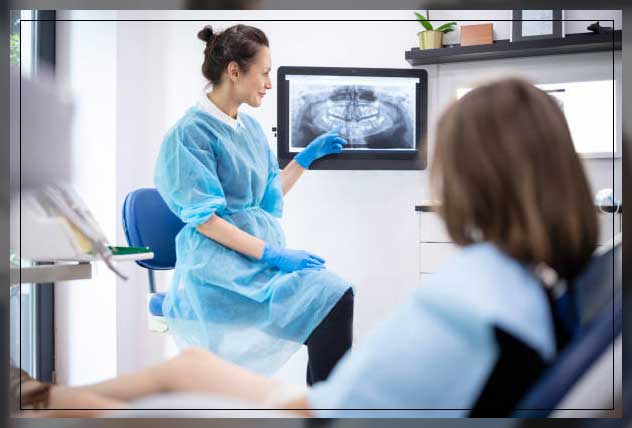
On the other hand, extraoral x-rays do not provide the detail of intraoral x-rays.
These are unable to identify the detail of individual tooth problems.
However, they can help detect impacted teeth, and monitor jaw growth, and development.
Furthermore, they can also help identify potential problems between teeth, jaws, temporomandibular joints, TMJ, or other facial bones.
Learn more about Dental Clinic Equipment List For Your Practice here.
Intraoral Radiographs
These are still one of the important imaging modules that are available dentists to and any dental practitioner.
The intraoral technique provides high spatial resolution or high resolution imaging of both teeth and potential associated dental and jawbone diseases.
Moreover, with careful attention to calibration and technique for detector positioning, these types help in diagnostic information for dental implant planning.
In addition to mesiodistal, i.e. horizontal, and crystal-apical, i.e. vertical measurements, they provide useful information on bone structure and density.
Another important thing to note is that these are the first step in dental checkups.
These can also provide a baseline standard against other radiographs.
You can then later compare them to monitor changes over time.
Marginal bone height is one of the most important methods for monitoring peri-implant bone health.
And it is still used as a measurement of implant success.
There are two types of radiation exposure techniques that you can use for intraoral periapical radiography:
- paralleling technique
- bisecting angle technique
With the parallel technique, the tooth and sensor are kept on parallel planes.
Also, this technique provides less image quality distortion and reduces excess tradition for your patients.
On the other hand, bisecting angle technique comes by placing the receptor as close to the tooth as possible.
The central ray systems of the x-ray beam is directly perpendicular to an imaginary line that bisects the angle it forms by the long axis of the tooth and the plane of the receptor.
You will need to use this technique in areas where parallel technique is impossible.
It can be due to poor access that can make the angle between tooth and films more than 15 degrees.
Learn more about Computed Radiography List here.
Types of Intraoral Radiographs
Types of intraoral dental digital radiography are:
Bitewing X-rays: You will take them when the patient bites down on the film.
This type helps to show the details of the upper and lower teeth in one area of the mouth.
Moreover, each bitewing shows a tooth from its crown, i.e. top to about the level of the supporting bone.
Bitewing X-rays help to detect decay between the teeth and changes in the bone density that occurs due to gum disease.
They also help to determine the fit of dental crowns or restoration and the marginal integrity of tooth fillings.
Periapical Or Limited X-ray: This helps to show the whole tooth from the crown to beyond the root tips to the supporting bone in one area.
it can either be the upper or lower jaw.
Furthermore, these types of x-rays help to aid in treating a condition like:
- periodontisits
- advanced gum disease
- detecting endodontic lesions or abscesses
Learn more about Dental Handpiece here.
Extraoral Radiographs
These help to show teeth, however, their main focus is the jaw and skull. These types of x-ray do not provide the detail that you can get with the help of intraoral x-rays.
Therefore, they cannot help detect issues like cavities or for identifying problems with individual teeth.
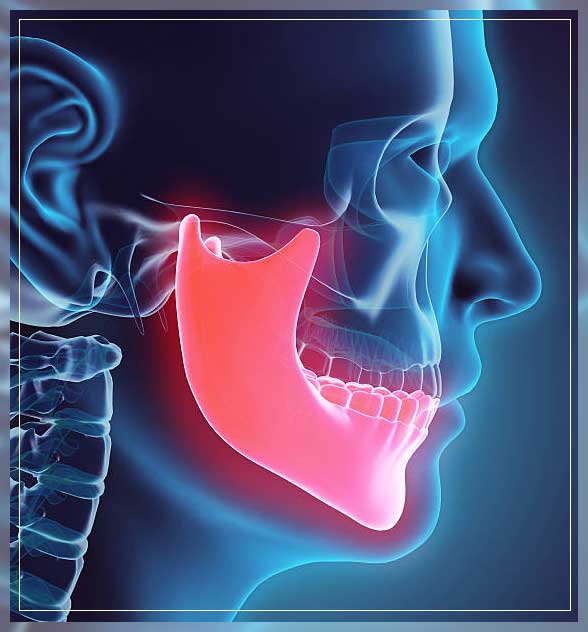
Instead, extraoral radiographs can help to look for:
- impacted teeth
- monitor growth and development of jaws in relation to the teeth
- identify potential problems between teeth and jaws
- the temporomandibular joint, or other bones of the face
Learn more about Dental Mouth Mirror here.
Types of Extraoral Dental Digital Radiographs
There are different types of extraoral radiographs. These are:
Panoramic X-rays help to show the entire mouth area, and the teeth in both upper and lower jaws on a single x-ray.
It helps to detect the position of full emerged teeth, as well as those that are emerging.
Moreover, it can help identify impacted teeth, and help in the diagnosis of tumors.
Tomograpm helps to show a particular layer or ‘slice’ of the mouth while blurring out the other layers.
This type is useful for examining structures that are difficult to see.
For instance, as other structures are in close proximity to the structure when you want to view them, you can use this type.
Celphalpmetirc Projections show the entire side of the head. it is important to note this type of x-ray helps to examine the teeth in relation to the jaw and profile of the individual.
Sialography involves the visualization of the salivary gland following the injection of a dye.
This dye is a radiopaque contrast agent, that you will inject into the salivary glands of the patients.
Moreover, these help to see the organ on an x-ray film.
Computed Tomography or CT scanning shows the interior structures as well as three-dimensional images of the body.
With this type of x-ray, you can identify problems in the bones of the face like tumors or fractures.
Learn more about Dental Chair: Types, Components, and More here.
Benefits of Dental Digital Radiography
Some of the benefits of digital dental radiography in comparison to traditional dental x-rays are as follows:
These help to reveal small hidden areas of:
- decay between the teeth or below the existing restorations,i.e. fillings,
- bone infections,
- gum or periodontal disease,
- abscess or cysts,
- developmental abnormalities,
- wisdom teeth removal
- and tumors
These are certain issues that are otherwise not detectable and can only be found with the help of visual dental examinations.
Moreover, they can help you view the x-ray instantly on the computer screen, and you can manipulate them to enhance contrast and detail.
You can also transmit them electronically to specialists without any quality loss.
Early detection and treatment of dental issues can help save time, money, and discomfort.
Digital mico-storage technology allows greater data storage capacity on small, space-saving drives.
Furthermore, these also help to eliminate chemical processing and disposal of hazardous wastes and lead foil.
Thereby, presenting a ‘greener’ and eco-friendly alternative to traditional x-rays.
Additionally, you can also transfer them easily to other dentists with compatible computer technology, or photo-printing with compatible technology.
It is important to note that the features of these dental digital radiographs include:
- contrasting
- colorizing
- 3-D
- sharpness
- flip
- zoom, etc
These also assist in diagnosis and patient education.
Lastly, you can store them in electronic patient records, send them to insurance companies, refer them to dentists or consultants, and often eliminate or reduce treatment disruptions.
Thus, it leads to faster dental insurance reimbursements.
Learn more about Lab Equipment: Essential Tools for Dentists here.
Disadvantages of Dental Digital Radiography
One of the most important things to note is that setting up dental digital radiography in your dental sitting can cost you more.
This is often more due to additional costs of the wired sensor systems, including maintenance and service repairs.
Moreover, many practices have more than one sensor and there is also a cost associated with personnel hours to convert old records to digital ones.
Implementing digital radiography in your dental practice also needs additional training that you need to periodically update to account for existing technology.
This is because, with advances in technology, it is quickly becoming either obsolete or unavailable.
The lack of dental digital radiography use is another disadvantage.
Some other disadvantages are:
Sensor Size: some direct sensors are thicker and bulkier than dental films which can cause discomfort.
This is especially for those who are prone to gagging.
Fragility: these are thinner than film plates, PSP plats are more prone to damage than needs frequent replacement.
Infection Control: a number of digital sensors and PSP phosphor plate can not be sterilized.
Therefore, they need protective plastic barriers that you will need to change between patients to prevent cross-contamination and infection.
Learn more about Sterilization and Disinfection here.
Special Training
Dentists, dental hygienists, dental assistants, and oral/maxillofacial radiologists may need to take dental digital radiographs ae special training.
Radiographic training requirements for your dental office personnel differ frequently from and are less stringent than those for medical x-ray personnel.
Moreover, these are also found in state dental practice acts or dental board regulations.
Some of the required training considerations are:
- periodic safety updates
- availability of and training in new equipment supplies and techniques
- infection control procedures
- continuing education in the proper and safe use of radiation equipment
- radiation doses
Learn more about Sterilizer Machine: Uses, Guidelines, and More here.
Safety Considerations
Though tradition exposure is low with dental digital radiographs, no one should receive more tradition than necessary. It is important that you and your staff use protective lead aprons and thyroid collars, especially in the case of pregnant women, women of childbearing years, and children.
However, it is safe for pregnant women to have up to four radiographs per office visit, though in most cases, you may want to delay radiographs until the pregnancy is over.
There are no corners for women conceiving in emergency situations. But make sure to take precautions and use double lead aprons to cut radiographic exposure to nearly immeasurable levels. While women who are breastfeeding or trying to conceive do not need to delay x-rays.