A D-dimer test helps to check for a small protein fragment that can help identify blood clotting problems.
A positive result can suggest a recent blood clot formation and breakdown in the body.
Moreover, it can indicate blood clotting conditions.
A function of blood clotting is a necessary process that can help to prevent you from losing too much blood after an injury to a blood vessel.
Moreover, the body of the patient forms a blood clot when a number of proteins join together at the site of an injury.
Once the site heals, the body prodcues another protein to break the clot into small pieces.
One of these protein fragments is D-dimer.
D-dimer is often not detectable in blood and is only present after the breakdown of a blood clot.
Therefore, a doctor or a healthcare professional can use a D-dimer test to find or identify an increase in the clotting mechanism of the body.
This can, in turn, help to identify a coagulation disorder.
Keep on reading to learn more about the D-dimer test.
D-Dimer Test
A D-dimer test is a blood test that helps to measure the level of D-dimer, a protein fragment that is present in the blood after the breakdown of a blood clot.
When a blood clot breaks down, it tends to produce fibrin degradation products, FDPs.
One of these FDPs is D-dimer.
It consists of different-sized pieces of crosslinked fibrin.

Moreover, this test can help helpful for indicate the presence of elevating clotting mechanism.
And it can help doctors and healthcare professionals in reaching a diagnosis.
However, D-dimer tests are very sensitive and can also result in false positives and negatives.
As such, this means that patients will need further tests that are necessary to accurately diagnose blood clotting disorders.
Conditions D-Dimer Test can help Diagnose
A D-dimer test can help doctors detect a number of blood clotting disorders.
These can include:
Pulmonary Embolism, PE
It refers to a blockage in the pulmonary artery that supplies the blood to the lungs.
An embolism describes when a blood clot travels to the blood vessels of the lungs and gets stuck, which can cause problems with the blood flow and gas exchange.
Moreover, it can also become a life-threatening event.
Deep Vein Thrombosis, DVT
This condition occurs when a blood clot or thrombus forms in a deep vein within the body of the patient.

DVT can have serious consequences, as the blood clot damages the valves in the vein, and the clot can also break free and result in a pulmonary embolism.
Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation, DIC
This condition describes a widespread hypercoagulable state.
And it can prevent blood from clotting normally.
Furthermore, this can compromise blood flow and can result in multiple organ dysfunction.
It can also help diagnose venous thromboembolism.
Who needs this Test?
A doctor can suggest a D-dimer test to patients when they suspect that they can have a blood clotting problem.
They can particularly recommend a lab test if an individual presents with DVT or PE symptoms like pain and swelling in the affected limb or labored breathing and chest pain.
In addition to the above, as it is a quick and noninvasive test, doctors and healthcare professionals can also use it to rule out these conditions.
Moreover, a healthcare professional can use this test along with other blood tests to reach a diagnosis.
In case a patient is undergoing treatment for DIC a doctor can use a D-dimer test to help monitor the condition of the patient.
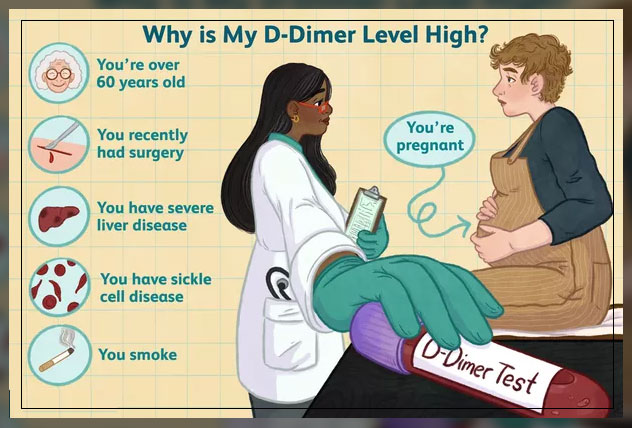
What Causes High D-Dimer?
It is important to note that a number of diseases, treatments, and lifestyle factors can raise D-dimer levels.
Patients with blood clots often have one or more of the same risk factors. These are:
Medical Conditions and Treatments
These include:
Heart Disease: Patients with unstable angina or those who have had a heart attack can have higher levels of D-dimer and a higher risk of future blood clots to form.
Cancer: Some cancers can also increase the risk of a blood clot.
Cancer Treatments: Chemotherapy and certain breast cancer drugs can increase the risk of clotting in the blood.
Treatment with Estrogen: Birth control pills and hormone replacement therapy can increase the risk of DVT and PE.
Surgery: Patients who undergo surgery like hip or knee replacement have a higher risk of a blood clot, while drugs doctors prescribe can help prevent this.
Infectious Diseases: COVID-19 and pneumonia can cause inflammation, thus, triggering blood clots.
Kidney Disease: For unknown reasons, kidney disease tends to increase the risk of DVT and PE.
Liver Cirrhosis: Patients with severe liver disease can also have a higher risk of clots in the large vein of the liver.
Pregnancy: D-Dimer tends to rise 2 to 4-fold by delivery.
Moreover, women can have an increase in the risk of DVT or PE for up to 3 months after delivery.
Other Risk Factors
Some other risk factors include:
Age: Patients over the age of 60 have a higher risk of blood clots
Smoking: Smoking increases the risk of blood clot formation.
Race: African Americans tend to have higher levels of D-dimer, in comparison to people of Europen Ancestry.
Gender: Women have higher levels of D-dimer than men
Weight: Obesity increases the risk of formation of blood clots
Sedentary Lifestyle: Not exercising or not moving for a long period of time can increase the risk of DVT or PE.
An example is a long plane ride or being in the hospital.
What to Expect?
To perform a D-dimer test, doctors or healthcare professionals will need a blood sample.
They will often draw the blood sample through needles from a vein in the arm of the patient.
As with any test that involves needles, it can carry a small risk of bleeding, infection, or bruising.
A patient may feel a slight stinging or painful sensation at the site where they will collect the sample.
Moreover, they do not need to prepare anything prior to the test.
After collecting the sample, the doctor or nurse will send it to a laboratory. Lab workers will then test that blood sample for the presence of D-dimers before returning the results to the doctor.
The doctor will then organize an appointment with the patients, where they can discuss the results and any further steps.
Learn more about Medical Diagnostic Imaging here.
Interpreting Results
A 2021 paper notes that a usual D-dimer blood level is less than 0.50.
As such, doctors and healthcare professionals consider a score of 0.50 or higher a positive result.
A positive result indicates atypically high levels of a protein that relate to blood clot formation and breakdown.
Moreover, this can suggest a blood clotting condition.
A typical result means that a patient does not have an acute blood clot or condition that causes atypical clot formation and breakdown.

While D-dimer tests tend to be sensitive, this means that can pick up existing blood clotting problems, that are not very specific.
This means that they can provide a positive result when there is no disease present.
A wide variety of factors can cause elevated D-dimer levels. These are:
- pregnancy
- cigarette smoking
- physical trauma
- cancer
- infections
- age
- being immobile
- having an autoimmune disease
Furthermore, a number of healthcare professionals can consider a D0dimer as an additional test.
When doctors discern that an individual or patient has elevated D-dimer levels, they can request further testing to reach an accurate diagnosis.
How does Clotting work?
Blood clotting is an important process that helps to prevent excessive bleeding.
When there is damage to a blood vessel, it gets smaller to let less blood through.
Moreover, platelets will immediately adhere to the injury and release certain chemicals that attract even more platelets forming a platelet plug.
Finally, clotting factor proteins work together to form threads of a protein, i.e. fibrin.
The fibrin threads then weave over the platelet plug to create a strong clot, which then allows the body to heal the injured blood vessel.
As part of the healing process, the body will begin to break the fibrin clot, which will release proteins like D-dimer.
Conclusion
Doctors and healthcare professionals can order a D-dimer test in case they suspect a patient to have a dangerous blood clot. This test helps them to rule out two conditions that can be fatal to the patients. These include deep vein thrombosis, in which a blood clot gets stuck in a deep vein, and pulmonary embolism, in which a blood clot is present in the lung.
A negative dimer test result means that the patient does not have a blood clot. Often, they will not need another test. However, if the results come back high, that does not necessarily mean that the patient has a clot. The test is not definitive, and doctors can likely order other tests to further evaluate the condition of the patient.
It is important to note that this is a fast, inexpensive blood test that helps to rule out a dangerous blood clot. However, a number of diseases, treatments, and lifestyle factors can increase the D-dimer levels. Thus, if the results are abnormal, the doctor will ask for or order more tests to confirm that the patient does not have a blood clot.