Esophageal pH screening is often ordered by doctors for patients with acid reflux or GERD.
The pH test for acid reflux or gastroesophageal reflux disease provides a number of measures of how stomach acid behaves in the esophagus of the patient.
It also includes how often it enters, how long it stays, and how well it clears out in the esophagus of the patient.
Moreover, the health care provider may order this test to confirm a diagnosis or to periodically monitor the reflux symptoms and treatment of the patients.
The doctor will use a thin, plastic tube with a sensor to diagnose and test a patient who may have GERD, one who is receiving treatment with a proton pump inhibitor, PPI medication, or has less common symptoms of GERD.
Keep on reading to learn more about pH screening.
Esophageal pH Screening
An esophagus pH test helps to measure how often stomach acid enters the esophagus of the patient.
The esophagus is a tube that connects your throat to the stomach.
Moreover, it also measures how long the acid stays there.
The test involves placing a catheter or a thin tube or a special device: a pH probe into the esophagus of the patient.
The catheter or device will measure the acid level or pH level for 24 to 96 hours.
Furthermore, it is important to note that the test can show if a patient has acid reflux or GERD.
Acid reflux is a disorder when the stomach acid flows back into the esophagus.
When the acid touches the esophagus, it can cuase a burning feeling or sensation in the chest or neck of the patient.
This is heartburn.
Acid reflux can also lead to GERD which is a more seriuos form of reflux.
While acid reflux or GERD is not life-threatening, the symptoms can be uncomfortable and affect the quality of life of a patient.
However, if the patient does not get treatment, GERD can damage the esophagus and lead to more seriuos health problems.
Some other names for pH Screening are:
- esophageal pH monitoring 24-hour esophageal pH test
- esophageal reflux monitoring
- acidity test
- pH monitoring
- pH probe study
Learn more about Medical Diagnostic Imaging here.
Uses of Test
A doctor can order an esophageal test to diagnose acid reflux or GERD.
However, a doctor can also order to see if the treatment for GERD is effective or not.
A patient may need this test if they experience the symptoms of acid reflux.
These symptoms are:
- heartburn
- swallowed food coming back into the mouth or regurgitation
- trouble swallowing
- feeling a lump in the throat
- sore throat
- cough
- frequent burping

Moreover, a doctor can use this test if the patient has GERD symptoms, but an endoscopy exam does not show any evidence of reflux disease.
In the case of the standard treatment of a twice-daily dose of proton pump inhibitor, PPI medication does not help.
Or when a patient experiences less common symptoms of GERD life chest pain, asthma, or hoarseness that needs to be evaluated.
Before testing the healthcare provider will also ask about symptoms of GERD like heartburn, nausea, or abdominal pain, chronic cough, or difficulty swallowing.
Furthermore, the health care provider will also ask the patient about the risk factors for GERD.
This includes whether the patient has a Hiatal hernia, smoke, take medications, or eat foods that can predispose them to reflux.
Learn more about Medical Equipment- Guide here.
Diagnosing GERD
In most cases, GERD diagnosis depends on the symptoms alone or a clinical diagnosis.
In case the diagnosis is uncertain or the symptoms a patient expereicnes are chronic or there are some concerns about complications, the doctor can recommend further testing.
Moreover, the standard test is an upper endoscopy for GERD.

During this test, the doctor will insert a tube through the mouth of the patient and into the esophagus and stomach of the patient.
In some cases, however, this test may show no evidence of abnormality to explain the symptoms a patient may be experiencing.
That is why the health care provider may recommend pH monitoring.
Learn more about Endoscopy procedures, Uses, and Types here.
Before the pH Screening
The doctor will instruct the patient to avoid eating after midnight before the procedure.
This is because some medications can affect the test results.
Therefore, the doctor will ask the patient to avoid taking some prescription or over-the-counter medications.
It is important for the patient to also discuss the above with the doctor as well.
Certain other medications that a patient may need to pause for the procedure are:
- adrenergic blockers
- antacids
- anticholinergics
- cholinergic
- corticosteroids
- H2 blockers
- proton pump inhibitors
The Procedure of pH Screening
To conduct a pH test, the health care provider will need to place a monitor into the esophagus of the patient to track acid levels.
There are two types of monitors that a doctor can use for this test: a catheter and a capsule.
Let’s discuss these two types as follows:
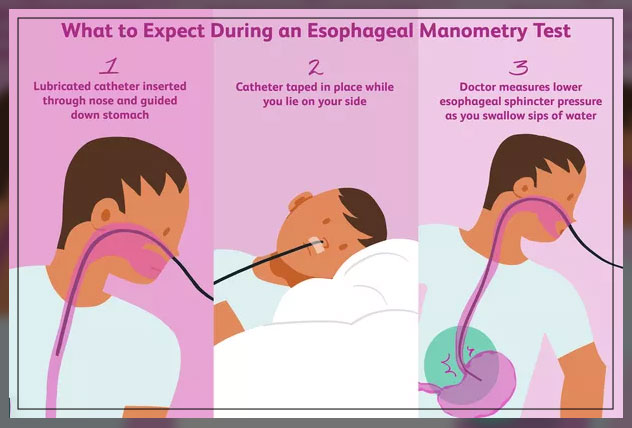
Catheter Test
The doctor will place the catheter using a scope.
Moreover, the healthcare provider will also place an IV and give the patient medication so that they can relax during the procedure.
However, in some cases, they may also spray the back of the throat of a patient with medications.
Then, they will insert a tube with a sensor through the mouth or nose and into the esophagus of th patient.
The sensor is then attached to the lining of the esophagus and the tube is removed.
The sensor will wirelessly send data to the monitor that the patient can wear either around the waist or shoulder.
Capsule Test
For this procedure, the patient will need to swallow a disposable capsule.
The capsule is about the size of a large pill.
This will travel down through the esophagus, stomach, and intestine of the patient.
It wirelessly records the data about the symptoms a patient experiences and when they eat or lie down.
One important thing to understand is that other types of sensors gather information about the symptoms a patient experiences.
The doctor will encourage the patient to engage in everyday activities and keep a diary of what they eat and any GERD episodes or suspected acid reflux issues and symptoms.
These can include coughing and wheezing.
Also, these will help the healthcare provider to determine if acid reflux is related to unexplained asthma or other respiratory symptoms.
After the Test
After the doctor places the monitor or the patient swallows it, the throat of the patient may feel slightly sore for a day.
Sucking n lozenges or hard candy can help soothe this discomfort.
Moreover, the sensor itself will not cause any pain or be detectable.
It will simply pass through the digestive tract of the patient and then be excreted without any problem.
The healthcare provider will receive the data gathered by the sensor and the diary entries.
Furthermore, the patient will need to schedule a follow-up appointment to review these results.
Interpreting Results
In most cases, the pH level in the esophagus should be close to 7.0/
Esophageal pH tests look for intervals in which the pH reaches lower levels like below 4.0.
This tends to be slightly acidic which means that the patient is experiencing a surge of stomach acid.
While abdominal results may also indicate GERD, an increase in stomach acid may also be due to conditions like:
- Barrett’s esophagus
- Dysphagia
- Esophageal scarring
- Esophagitis

However, if the pH monitoring results show that the pH of the patient is normal, but still they are experiencing GERD symptoms, the doctor can recommend another type of test.
These tests may include barium swallow or an upper endoscopy.
Depending on the results of the test, the health care provider may recommend lifestyle changes and medications.
These will help to ease the symptoms and prevent complications.
Is there anything else a Patient should know?
When a doctor diagnoses a patient with acid reflux or GERD, they may need to reduce or eliminate the symptoms with diet and lifestyle changes.
Diet changes include limiting foods that are fatty, spicy, citrus fruits, and juices, tomatoes, and tomato products, and alcohol.
While lifestyle changes include eating smaller amounts of food, quitting smoking, waiting a few hours after eating before a patient lie down, and losing weight if needed.
Moreover, over-the-counter medicine may also be helpful. These include antacids.
In case the symptoms a patient is experiencing is does not improve or are more serious, the provider may recommend treatment to reduce or block acid production.
These can include over-the-counter and/or prescription medications.
In some cases, however, the doctor can recommend surgery for more severe and/or persistent symptoms.
Final Thoughts
The esophageal pH screening shows how much stomach acid enters the esophagus and how long it remains there. It is an important test that helps the doctor to diagnose or monitor GERD.
However, they can also use this screening test to help the patient manage their symptoms or to identify other possible health conditions that could be causing GERD-like problems.
Therefore, it is important for the patient to visit or seek medical advice in case they are esperiencing persistent or severe symptoms. In such cases, the doctor may recommend surgery to ease the symptoms.