During the time of the Coronavirus pandemic, many patients require an oxygen cylinder.
It helps patients breathe who face oxygen deficiency and are unable to inhale it on their own.
The cylinders alongside oxygen concentrators are a means of giving oxygen therapy.
These supply oxygen to the body whether you are in the hospital, at home or are being transferred to a hospital.
This article discusses the different types of oxygen cylinders and why they are such crucial medical equipment that you can also keep at your home. Keep reading below to know more.

What is an Oxygen Cylinder?
One of the crucial roles of the lungs is to inhale oxygen and let out carbon dioxide from the body.
However, the lungs and their respiratory function are poorly impacted in diseases such as the coronavirus.
In that case, oxygen deficiency occurs when the membrane that lets out carbon dioxide and allows oxygen inside is affected.
Thus, it leads to oxygen deficiency in the body.
Hence, you will need external oxygen therapy or an administration system to assist breathing.
For that purpose, there are both oxygen concentrators and cylinders.
In simple terms, an oxygen tank is a medical equipment that provides supplemental oxygen to the patient via a surgical mask, oxygen rebreather or nasal cannula.
It is a storage container with different capacities. This brings us to…
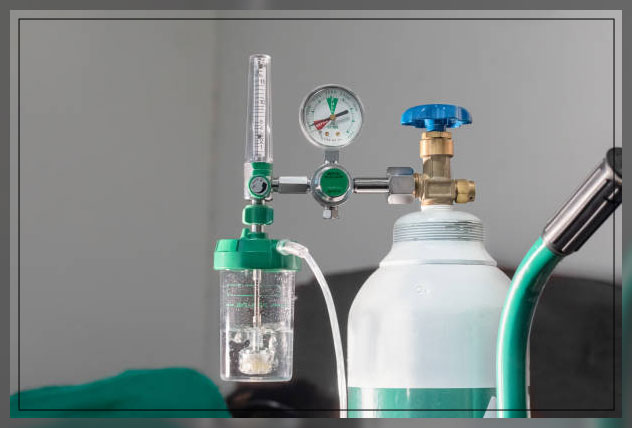

The Types of Oxygen Cylinders
Material
Technically oxygen tanks are not only for medical purposes.
They are also popular in industrial use.
Usually, these are made up of steel and aluminum.
When it comes to the material, aluminum cylinders are lighter in weight than steel.
Hence, it is easier to transport them or carry them around.
Form of the Gas
The oxygen in the cylinder is in liquid or gaseous form.
The liquid form is in a cryogenic storage tank which contains 99.5 percent pure oxygen.
Oxygen gas is first cooled to –182.8°C to turn into a liquid state.
The cryogenic storage tank is a special tank that continues to keep the liquid cool.
It is when the liquid comes across warmer temperatures that it changes state back to gas.
The gas then flows outwards through the oxygen delivery device.
It is less bulky to store than the second type, compressed oxygen.
However, it requires training as well as special equipment so its use is not as common.
In a compressed oxygen gas cylinder, the aluminum tanks are filled with oxygen extracted from the air.
It is first compressed and then it fills aluminum tanks with a capacity of 2200 per square inch PSI of pressure.
As the gas is released, the high pressure of the tank forces the gas out through the oxygen delivery system with a mask or nasal tube.
This also contains about 99.5 percent pure oxygen.
Capacity
The oxygen-filled in liters differentiate the tanks from each other.
Steel oxygen cylinders are available in:
- 1 liter
- 2 liter
- 3 liter
- 5 liter
- 10 liter
- 20 liter
- 27 liter
- 40 liter
- 50 liter
Whereas aluminum cylinders have the following capacity:
- 1 & 2 liter
- 3 &4 liter
- 5 & 10 liter

How Does It Work?
This tank consists of a flow regulator knob, nasal cannula, cylinder, pressure gauge, humidifier bottle, adapter and surgical mask.
To deliver supplemental oxygen to patients who cannot inhale it on their own, you can check the required amount using a pulse oximeter.
Other than these, there is a flow regulator on the top.
It converts the pressurized oxygen into a flow that is measurable in liters per minute or LPM.
This includes the pulse-dose flow regulators and continuous flow regulators.
- Pulse-dose flow: This flow increases the effectiveness of the cylinder. It releases only short bursts of oxygen whenever you inhale through the mask. The oxygen is not wasted here. The machine should be set to the prescribed LPM for use.
- Continuous flow: The other is the continuous flow regulator which sets a specific LPM. Unlike Pulse-dose flow that releases short bursts, it dispenses the same level of oxygen throughout. This happens till it is shut off or the tank runs out of supply. It is ideal for patients who require oxygen on an intermittent basis.
When Should You Use It?
A person with low oxygen blood levels will require supplemental oxygen.
However, an individual should only consider using it after a certified medical professional advises to use it.
A pulse oximeter can monitor blood oxygen levels regularly.
One healthy individual will have normal oxygen saturation SpO2 of around 92 to 95 percent.
Levels that fall below 92 percent may need supplemental oxygen.
If the individual is already suffering from a lung disease, the doctor will decide whether they need the tank at home or they should come to the hospital for treatment.
Besides that, they will analyze how frequently and for how long the individual will require oxygen therapy to remain healthy.
Let’s know about handling it.
Steps on Using It
Now you are already aware of the components of an oxygen cylinder, let;s find out how to handle it especially if you are at home.
- Begin by using clean hands and checking if the cylinder is clean too. There should be no damage, grease or oil on it.
- First, attach the regulator to the valve present at the top of the tank.
- Turn the tank on using the valve or the cylinder wrench.
- As the valve opens it is time to check the contents gauge. This will check the pressure to tell if there is sufficient oxygen gas present on the tank.
- Now you can make adjustments to the flow of the gas to the required LPM. For this use the control on the flow regulator knob. Remember to check that oxygen has begun flowing.
- Move to the oxygen outlet and attach the nasal tubes, nasal prongs or oxygen mask as you require. It is crucial to adjust the nasal prongs so they comfortably attach to the patient.
- Ensure everything is ready to use, the tubes and masks are working properly and then finally put them on.
- While using nasal tubes, position these upwards in the nostrils while looping them over the ears. Moreover, use the tube adjuster to tighten its position under the chin.
- For mask, simply place it over the mouth and nose. Secure it in place by placing the band, around the ears or behind the head. Ensure that there are no gaps especially on the sides and edges that may result in a leak.
- After you are done using it, turn it off. Store it in a horizontal position while in its carrier. Ensure that it is firmly secured so that it doesn’t roll around and remains in position.

Oxygen Cylinder vs Oxygen Concentrator
Both of these medical devices and equipments provide oxygen therapy to patients.
However, their method of delivery can be very different.
Oxygen cylinders are generally in more common use than the concentrators.
Let’s find out about their differences.
Working
Oxygen Cylinder: Has a fixed and finite amount of compressed oxygen that the user inhales. It eventually runs out after use and the tank is emptied.
Oxygen Concentrator: Its mechanism generates an infinite supply of oxygen. This is because it filters oxygen present in the surrounding air to make medical grade oxygen using the battery that powers the whole mechanism has life.
Portability
An oxygen cylinder has portable versions available, whereas an an oxygen concentrator is already portable.
Flow Regulators
Oxygen Cylinder: Deliver oxygen through continuous flow.
Oxygen Concentrator: Depends on the device. Some portable options deliver oxygen through the pulse-dose flow.
Method of Oxygen Delivery
Both the cylinders and the concentrators use a surgical mask or a nasla tube to deliver the oxygen to the patient.
Replacement and Refilling
Oxygen Cylinder: The oxygen supply present in the cylinder is compressed. Hence, the supply runs out gradually as it is used. Thus, you need to refill or replace it as the tank empties.
Oxygen Concentrator: The concentrator, however, does not need replacing or refilling. In fact, it works similar to how an air conditioner does. It takes in air, filters and modifies it to deilver in a new way and form of gas. Thus, there is no need to replace and refill it. Moreover, you also gather why there is an infinite supply in a concentrator because the dosage method varies from that of a cylinder.
Considerations While Buying
While choosing the ideal oxygen cylinder for your use, consider the following:
- Size, compact and portable or high volume and stationary
- Need continuous flow of delivery of pulse-dose that delivers oxygen according to the breathing pattern of the patient
- The amount of time you need to use it
- Do you want a cylinder or concentrator?
You can also choose both.
Portable and smaller models of cylinder can come in use with a concentrator that keeps refilling the cylinder with home-fill system.
This way, you can utilize the good qualities of both of these to receibve oxygen supply aptly without running out of it often.
Choose according to what your doctor suggests are the patients’ needs and requirements.
If you wish to look into medical and dental prodcuts, visit our shop for more.
Finally,
Be careful while you are handling the oxygen cylinder.
Too much or too little oxygen can lead to toxicity or hypoxia.
Moreover, it needs cleaning, care and maintenance to prevent buildup of fungus and bacteria that can cause infections.
Also remember these are highly combustible so keep them away from flames. Neither use products like aerosols, petrolem products and oil-based face creams around an oxygen cylinder.