Do you know that latex allergy is common when you wear anything that is made of it?
Latex is natural rubber from the milky sap of the Brazilian rubber tree Hevea brasiliensis.
Moreover, you can find it in a number of products like medical gloves, and IV tubing.
Similar proteins are also present in different popular foods.
An allergy occurs when your immune system reacts to an otherwise harmless substance and treats it as an invader.
it can be a virus or bacteria.
A host of antibodies and chemicals including antihistamines are released. These race to the point of invasion where they cause an anti-inflammatory immune response.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, latex allergies affect about 1 to 6% of Americans.
An allergic reaction to latex may range from mild to severe; in some cases, it can even be life-threatening.
The key is to prevent your exposure as much as possible, though you may have exposure at the office or workspace.
Make sure to avoid the symptoms. You can do so by taking a few extra precautions.
While making sure to ask your allergist whether or not your case is severe enough to warrant medical treatment.
Keep on reading to learn more about latex allergy.
Symptoms of Latex Allergy
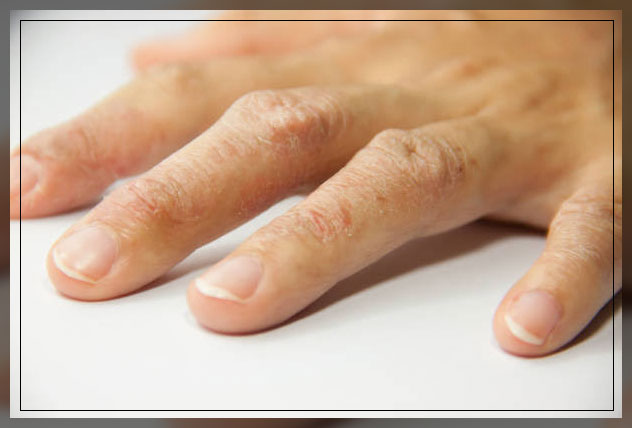
Allergic reactions to latex, in most cases take a form of a rash at the point of contact.
This is also known as allergic contact dermatitis.
Signs may include itchy hands, a skin rash that may be warm to the touch, hives, and eczema.
Eczema is also denoted as weeping or cracking skin.
Moreover, it is important to note that such reactions are often temporary and can begin within minutes of exposure.
However, they can also take a number of hours to develop.
You may need hydrocortisone cream or calamine lotion to soothe any rashes that develop.
Latex protein, in some cases, can also be airborne.

When this happens, a hypersensitive person may unknowingly breathe them in and develop more severe reactions.
These can include the following:
- swollen and red skin, lips, or tongue
- runny or stuffy nose
- shortness of breath with or without wheezing
- abdominal pain
- vomiting
- rapid heartbeat
- dizziness
Anaphylaxis is a rare reaction to latex and can be life-threatening.
The symptoms of this are just like that of airborne sensitivities, however, much more severe.
Anaphylactic shock can cause severe breathing difficulties, a decrease in blood pressure, or even death if you do not get treatment.
Learn more about Types of Wound Dressings here.
Products that Contain Latex
It is important to note that there are hundreds of products that contain latex.
These also include most times that you can stretch.
Thus, you can try avoiding them to avoid latex allergy:
Medical devices like gloves, intravenous tubes, catheters, and blood pressure cuffs contain latex.
Dentistry devices such as orthodontic rubber bands and dental dams contain it.
Contraceptive products like condoms and diaphragms, and clothing that contain elastic bands like
- pants or underwear
- running shows
- raincoats
Moreover, certain household products like zippered storage bags, bathmats, some rugs, and rubber gloves.
Infant and children items like pacifiers, bottle nipples, disposable diapers, and teething or other toys.
Certain school or office supplies like rubber bands, erasers, adhesive tape, rubber cement, and pain.
Elastic bandages like Band-Aid brand bandages, and rubber balloons.
However, mylar balloons are fine.
Latex cross-activity with certain Foods
According to the estimates of the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology, 50% of people with latex allergies also have other kinds of allergies.
Moreover, some people people who are allergic to latex can also have an allergic reaction to certain foods that contain a protein similar to the one present in latex, causing food allergies.
This is known as cross-activity.
Fruits and Vegetables
The following foods can cause a cross-reaction in some people, while different foods tend to have different degrees of association with cross-reactions.
Foods with a high association are:
- avocadoes
- banans
- kiwi
While foods with a moderate association are:
- apples
- carrots
- celery
- papayas
- melons
- tomatoes
- potatoes
Foods with a low association are cherries, figs, grapes, nectarines, pineapple, strawberries, and plums
Other Foods
Another important thing to note is that you should be cautious of the other potentially cross-reactive foods.
These are tree nuts, and legumes including almonds, cashews, chestnuts, hazelnuts, peanuts, pecans, and walnut.
Moreover, grains include wheat and rye, and shellfish include crab, lobster, and shrimp.
In case you have a reaction to any one of the above foods, discuss it with your doctor.
People who are at a great Risk for Latex Allergy
There are a number of healthcare workers that are affected by latex allergies.
In fact, the number is much higher than average.
According to the estimates of the Asthma and Allergy Foundation, about 8 to 17% of all healthcare workers have this allergy.
Moreover, an increase in use and repeated exposure to latex is thought to be the main reason for the higher rates in this group.
While others that are at an increased risk of latex allergy are:
- people with food-related cross-allergies
- hairdressers
- children who have spina bifida or one with multiple surgeries
- those who need frequent medical procedures like catheterization
- childcare provides
- food service provides
- housekeeps
- those who work in rubber manufacturing or tire factories
Diagnosing Latex Allergy
In some cases, diagnosing this allergy can be challenging.
Your doctor will examine your skin and ask questions about your symptoms and medical history.
Therefore, tell your doctor about your reactions to latex and if you have had any other allergy signs and symptoms.
Your doctor will also ask you questions that will help them to rule out other reasons for your symptoms.
With the help of a skin test, your doctor can determine whether your skin reacts to latex or not.

During this test, they will use a tiny needle to place a small amount of latex below the surface of the skin on either your forearm or back.
In case you are allergic to latex, you will develop raised bumps.
However, only an allergist or other doctor with experience in skin testing should perform this test.
Moreover, with the help of a blood test, your doctor can also check for latex sensitivity.
Treatment Options
Though medications are available to reduce the symptoms of latex allergy, there is, however, no cure.
The only way to prevent latex allergy reactions is to avoid products that contain latex.
Moreover, despite your best efforts to avoid latex, you may come in contact with it.
In case you have a severe allergic reaction to latex, you may need to carry injectable epinephrine with you all the time.
Furthermore, if you have an anaphylactic reaction, you will need to go to the emergency room for an immediate injection of adrenaline or epinephrine.
For less severe reactions, your doctor can prescribe antihistamines or corticosteroids which you can take after exposure to latex.
These will help you to control the reaction and help relieve discomfort.
Reducing the Risks
It is important to note that latex is so common in the modern world that it can be difficult to completely avoid exposure.
Still, you can take certain steps to reduce contact. These are:
- using non-latex gloves like vinyl gloves, powder-free gloves, hypoallergic gloves, or glove liners
- telling daycare and healthcare providers including dentists about any latex allergies
- wearing a medical ID bracelet detailing allergies
Prevention Tips
A number of products contain latex, however, you can find a suitable option.
To prevent an allergic reaction to latex avoid dishwashing gloves, some types of carpeting, balloons, rubber toys, hot water bottles, baby bottle nipples, and some disposable diapers.

Moreover, avoid rubber bands, erasers, condoms, diaphragms, swim goggles, racket handles, motorcycle and bicycle handgrips, blood pressure cuffs, stethoscopes, and syringes.
You should also avoid:
- intravenous tubing
- respirators
- electrode pads
- surgical masks
- dental dams
A number of health care facilities use non-latex gloves.
However, as other medical products may contain latex or rubber, make sure to tell the doctors, nurses, dentists, and other healthcare workers about the allergy before all exams and procedures.
Wearing a medical alert bracelet can help inform others about your allergy.
Final Thoughts
Latex allergy is a reaction to certain proteins naturally found in natural rubber latex, which is a product that comes from the rubber tree. If you have this allergy, your body will mistakenly take latex as a harmful substance and react to it.
It can cause itchy skin and hives, while in severe cases anaphylaxis. This is a life-threatening condition that can cause throat swelling and severe difficulty breathing. Your doctor can find out if you have a latex allergy or whether you are at risk of developing a latex allergy or not.
Moreover, these allergies are life-threatening. The key to preventing the symptoms is to limit the exposure as much as possible. Though it can be easier said than done, however, if you can be exposed to latex at work. Still, you can avoid symptoms without changing your lifestyle if you take a few extra precautions. Therefore, make sure to ask your allergist in case your case is severe enough to warrant medical treatment.