When a patient with failed or damaged kidneys face difficulty eliminating waste and unwanted water from the blood the doctor can recommend Kidney Dialysis.
Kidney dialysis is an artificial way of carrying out this process.
Moreover, dialysis substitutes the natural work of the kidneys of humans. Therefore, it is also known as Renal Replacement Therapy, PPT.
It is important to note that healthy kidneys help to regulate th levels of water and minerals and remove waste in the body.
The kidneys also secrete certain products in metabolism, however, dialysis cannot do this.
A person who has lost 85 to 90% of their kidney function will be a likely candidate for dialysis.
Around 14% of the population of the United States is thought to have chronic kidney disease, CKD.
Keep on reading.
Kidney Dialysis
The kidneys of a healthy person filter around 120 to 150 quarts of blood each day.
However, if the kidneys are not working correctly, waste tends to build up in the blood.
Eventually, this can lead to coma and even death.
Moreover, the cause may be a chronic, or long-term condition or an acute condition like an injury or a short-term illness that affects the kidneys.
Kidney dialysis helps to prevent the waste products in the blood from reaching hazardous levels.
Furthermore, it can also help remove toxins or drugs from the blood in an emergency setting.
There are different types of dialysis. The three main approaches are:
- intermittent hemodialysis, IHD
- peritoneal dialysis, PD
- continuous renal replacement therapies, CRRT
It is important to note that the choice depends on factors like the situation of the patient, availability, and cost.
Learn more about Medical Items: Guide here.
Intermittent Hemodialysis
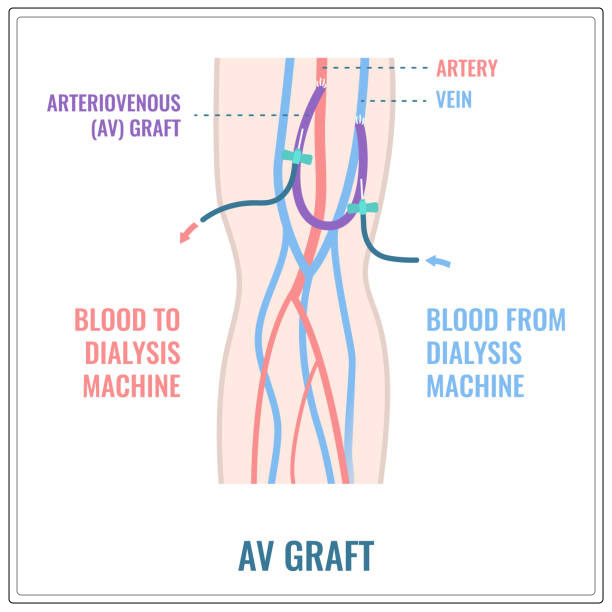
During hemodialysis, the blood will circulate outside the body of the patient and goes through a machine with special filters.
The blood will come out of the patient through a flexible tube, i.e. catheter.
This tube is inserted into the veins of the body of the patient, like a vein in your neck.
Like kidneys, the filters will remove the waste products from the blood.
Then the filtered blood will return to the patient through another catheter. The symptoms work like an artificial kidney.
Moreover, patients who are going to have hemodialysis treatment will need surgery to enlarge blood vessels, often in the arm.
Enlarging a vein will make it possible to insert the catheters.
Hemodialysis is often done three times a week, for 3 to 4 hours a day.

It depends on how well the kidneys of a patient are working and how much extra fluid weight they are gaining between dialysis treatments.
The doctor can do hemodialysis in a special dialysis center in a hospital or dialysis at home.
People who have, however, dialysis at him, or their caregiver, must know what to do.
If a person does not feel comfortable or confident doing hemodialysis at home, they can attend sessions at the hospital.
According to the National Kidney Foundation, home hemodialysis is suitable for people who:
- have been in a stable condition while on dialysis
- do not have any other disease that can make home hemodialysis unsafe
- have suitable blood vessels for inserting catheters
- have a caregiver who is willing to help with the hemodialysis
Furthermore, the home environment must also be suitable for taking the equipment for hemodialysis.
Learn more about Sterilization and Disinfection here.
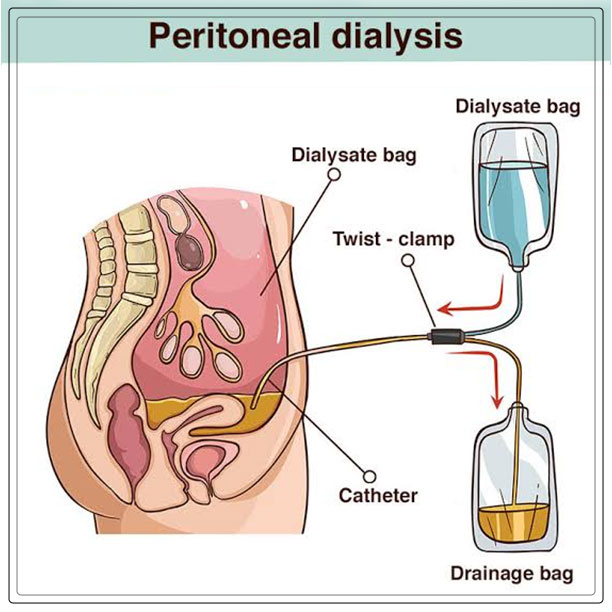
Peritoneal Dialysis
While hemodialysis helps to remove impurities by filtering the blood, peritoneal dialysis tends to work through the process of diffusion.
In peritoneal dialysis, a sterile dialysate solution that is rich in minerals and glucose will run through a tube into the peritoneal cavity, the abdominal body cavity, that surrounds the intestine.
Moreover, it has a semi-permeable membrane, the peritoneal membrane.
It is important to note that peritoneal dialysis uses the natural filtering ability of the peritoneal, the internal lining of the abdomen, to filter the waste products from the blood.
The dialysate is left in the peritoneal cavity for some time so that it can absorb waste products.
Then the doctor or health professional will drain it out through a tube and discard it.
This exchange or cycle is normally repeated a number of times during the day and the doctor can also perform it overnight with an automated system.
The elimination of unwanted water or ultrafiltration tends to occur through the process of osmosis.
The dialysis solution will have a higher concentration of glucose and this causes osmotic pressure.
Additionally, this pressure then causes the fluid to move from the blood into the dialysate.
As a result, more fluid drains than is introduced.
It is important to note that peritoneal dialysis is less efficient than hemodialysis and can take longer periods and removes about the same amount of:
- total waste products
- salt
- water
However, peritoneal dialysis can give patients more freedom and independence as they can either do it at home instead of going to the clinic several times.
They can also do it while traveling with a minimum of specialized equipment.
Before starting peritoneal dialysis, the patient will need a small surgical procedure to insert a catheter into the abdomen.
The doctor will keep it close, except when they need to use it for dialysis.
Types of Peritoneal Dialysis
There are two main types of peritoneal dialysis.
Let’s discuss them as follows:
Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis, CAPD
This type requires no machinery and the patient or caregiver can also do it.
The doctor will leave the dialysate in the abdomen for up to 8 hours and then replace it with a fresh solution straight away.
Moreover, this will happen every day, four to five times per day.
Continuous Cyclic Peritoneal Dialysis, CCPD, or Automated Peritoneal Dialysis
This type tends to use machinery to exchange fluids and the doctor often will do it every night while the patient sleeps.
It is important to note that each session will last for 10 to 12 hours.
After spending the night attached to the machine, most people will need to keep the fluid inside the abdomen during the day.
While some patients may need another exchange during the day.
A peritoneal dialysis is a suitable option for patients who may find hemodialysis too exhausting like elderly people, infants, and children.
Furthermore, it can also be done while traveling, so it is more convenient for those who work or attend school.
Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy
It is important to note that dialysis can either be intermittent or continuous and depends on the stage renal disease is in.
While a session of intermittent dialysis tends to last for up to 6 hours, continuous renal replacement therapies, CRRT is designed for 24 hours and used in an intensive care unit, ICD.
There are, however, different types of CRRT.
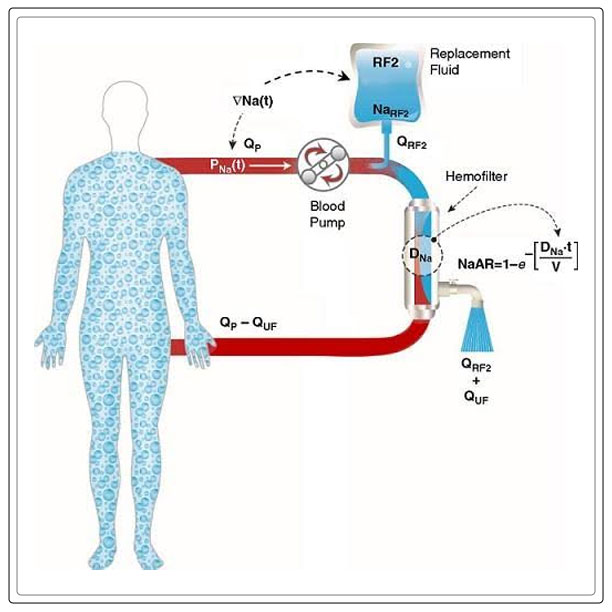
It can involve either filtration or diffusion.
It is better tolerated than intermittent dialysis, as the solution or fluid removal tends to be slower.
This leads to fewer complications, for instance, a lower chance of hypotension.
Temporary Dialysis
In some cases, a patient may receive kidney dialysis for a limited period of time.
People who may benefit from temporary dialysis are those who have a:
- sudden or acute kidney condition
- consume toxic substances or take a drug overdose
- a traumatic injury to the kidney
- chronic heart disease
While risks and complications are hypotension, cramps, nausea, and vomiting, headache, chest pain, back pain, itchiness, fever, and chills.
However, in some cases, the kidneys remove and do not need further treatment.
Does Kidney Dialysis replace the Kidneys?
Kidney dialysis helps patients whose kidneys have failed, however, it is not as efficient as a normal kidney.
Patients who will receive kidney dialysis need to be careful about what and how much they drink and eat, and will need to take medication.
A number of people who have dialysis normally have difficulty becoming pregnant and there will be a higher level of waste products in the body.
This is in comparison to normal kidneys and will interfere with fertility.
Women who do become pregnant while on dialysis will need an increase in dialysis during pregnancy.
However, if a woman has a successful kidney transplant, her fertility will return to normal.
Dialysis has some effect on male fertility, but less than on female fertility.
Learn more about Pregnancy Tests: Blood Tests, Kits, Ultrasound, And More here.
Symptoms of Kidney Failure
Symptoms of Urosepsis are:
- pain near kidneys on the lower sides of the back
- nausea without or with vomiting
- extreme fatigue
- reduction in urine volume or no urine
- trouble breathing or rapid breathing
- confusion or brain fog
- unusual anxiety levels
- changes in heart rate like palpitations or a rapid heartbeat
- high fever or low body temperature
- profuse sweating
- weak pulse

However, in some serious cases, urosepsis can progress to severe sepsis, septic shock, or multi-organ failure.
People with severe sepsis tend to produce little to no urine and may have difficulty breathing and their hearts may also have difficulty functioning.
Moreover, during septic shock, the blood pressure of the person can drop to extremely low levels and their organs may shut down.
These symptoms are life-threatening and will require immediate medical attention.
Causes and Risk Factors
A UTI can occur if bacteria enter through the urethra which is the tube that urine travels through to exit the body.
These bacteria may reach the urethra in a number of ways including through sexual contact, inadequate personal hygiene, or a pre-existing bladder condition.
However, women are more prone to UTIs than men as their urethras are shorter than that of a man.
The bacteria can spread from the urethra into the bladder where they will multiply, thus, causing infection.
If patients do not get treatment, it can lead to complications like urosepsis.
In some cases, UTIs develop due to bacteria that are already present in the bladder multiplied to an unhealthy level.
Risk Factors
Some people, including women and older adults, are at great risk of developing urosepsis.
Moreover, people with open wounds or devices like catheters or breathing tubes are also at risk of getting infections and UTIs.
These can increase the risk of urosepsis.
While other risk factors for urosepsis are:
- diabetes
- age over 65
- a compromised immune system from autoimmune disorders like HIV or AIDS
- immunosuppression from certain drugs like organ transplants or chemotherapy
- corticosteroid treatment
- history of urinary conditions
- use of catheter
Side Effects of Kidney Dialysis
Patients who depend on n kidney dialysis may experience:
- muscle cramps
- itchy skin, that may worsen before or after a procedure
- low blood pressure, especially in people with diabetes
- sleep problems, in some cases, due to itchiness, restless legs, or small breaks in breathing, i.e. apnea
- fluid overload, so patients can consume a fixed amount of fluid each day
- infections or ballooning at the access site for dialysis
- depression and mood fluctuation
It is important to note that kidney disease is a seriuos condition and in people with chronic kidney failure, the kidneys are unlikely to recover.
However, dialysis can help enhance well-being and prolong life for up to 20 years or more.