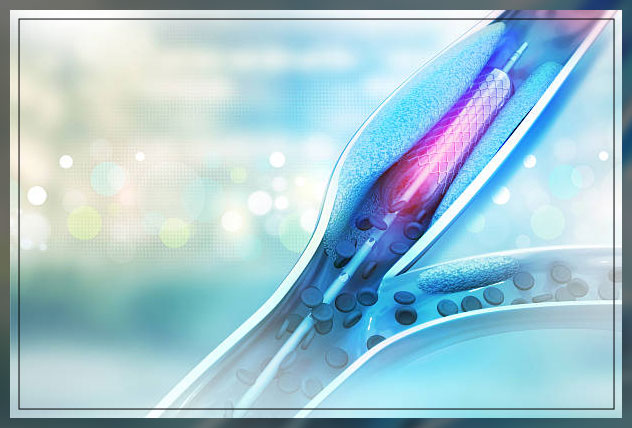
In case a patient has a restriction in blood flow, the doctor will order a peripheral artery angioplasty procedure.
Peripheral artery angioplasty is a medical procedure that helps blood flow better.
Moreover, the procedure helps to widen or open narrowed blocked heart arteries, often in the pelvis or legs.
This can help with pain or wounds to heal better and percutaneous coronary intervention.
It is important to note that the parties of the patient can narrow down due to plaque which is the buildup of fats in the arteries.
While the patient may be awake for the procedure, the medicine doctors administer helps to prevent pain and relax the patient.
Keep on reading to learn more about angioplasty and stent placement in detail.
Angioplasty Procedure and Stent Placement
Angioplasty procedure with stent placement is a minimally invasive procedure that helps to open a narrow or blocked coronary artery.
Doctors can use this procedure in different parts of the body of the patient, according to Braunwald Heart, Lung and Blood Institute.
Moreover, it depends on the location of the affected artery. It only requires a small incision.
It is important to note that angioplasty is a medical procedure in which the surgeon will use a tiny balloon to widen an artery.
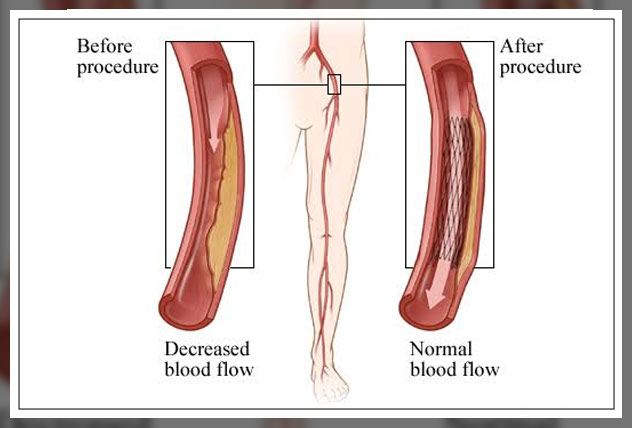
A stent on the other hand is a tiny mesh tub that they will insert into the artery of the patient and leave it there to prevent it from closing.
Also, the doctor can recommend taking aspirin or antiplatelet drugs like clopidogrel, or Plavix to prevent clotting around the stent.
Or they may prescribe medications to help lower the cholesterol of the patient.
Learn more about Infection Control and Prevention Guidelines here.
Use of Angioplasty Procedure
When the cholesterol levels of the patient are high, a fatty substance known as plaque tends to attach to the walls of the arteries.
This is Atherosclerosis.
As plaque accumulates on the sides of the arteries of the patient, the arteries can narrow and this tends to reduce the space available for blood to flow.
Moreover, plaque can accumulate anywhere in the human body, including the arteries in the arms and legs.
The arteries and other arteries farthest from the heart as Peripheral Arteries.
Angioplasty procedure and stent placement in the body of the patient are treatment options for peripheral artery disease, PAD, and coronary artery disease.
This common condition involves the narrowing of the arteries in the limbs of the patients, according to the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute.

The symptoms of PAD include:
- a cold feeling in the legs
- color changes in the legs of the patient
- numbness in the legs
- cramping in the legs after activity
- erectile dysfunction in men
- pain that tends to relieve with movement
- sores in the toes of the patient
In case medication and other treatments do not help with PAD, the doctor or health care professional may opt for an angioplasty procedure and stent placement.
Doctors can also use it as an emergency procedure if the patient has a heart attack or stroke.
Potential Risks of the Procedure
It is important to note that any surgical procedure carries risks. These risks are also associated with angioplasty procedures and stents.
These include:
- allergic reaction to a medication or dye
- breathing problems
- bleeding
- blood clots
- infection
- kidney damage
- re-narrowing of the artery or restenosis
- rupture of the artery of the patient
However, the risks that come with angioplasty are small. Still, they can be serious.
The doctor will help the patient evaluate the benefits and risks of the procedures, according to the 2013 ACCF AHA guideline for the management of st elevation myocardial infarction.
In some cases, they may also prescribe anticlotting medications like aspirin for at least a year after the procedure.
Preparing for Angioplasty Procedure
There are a number of ways in which a patient can prepare for the procedure.
The patient should do the following:
- inform the doctor about any allergies they may have
- tell the doctor about the drugs, herbs, or supplements they are taking currently
- tell the doctor about any illness they have, these can include common cold or flu, or any other preexisting condition like diabetes or kidney disease
- avoid eating or drinking, including water, the night before the surgery
- take any medication the doctor will prescribe to the patient
Procedure of Angioplasty
Angioplasty with stent placement often takes at least one hour.
However, the procedure can also be longer if the doctor needs to place the stent in more than one artery.
The doctor will administer local anesthesia to help relax the body and mind of the patient.
While most people tend to be awake during the procedure, they will not feel any pain. The different steps of the procedure are:
Making the Incision
Angioplasty with stent placement is a minimally invasive procedure that the doctor will perform through a small incision, often in the groin or hip of the patient.
The goal is to create an incision that will give the doctor access to the blocked or narrowed arteries that are causing the health issues of the patient.
Locating the Blockage
Through the incision, the surgeon will insert a thin, flexible tube: Catheter.
Then they will guide the catheter through the arteries to the blockage.
During this step, the surgeon will view the arteries using a special X-ray: Fluoroscopy and the doctor may also use a dye to identify and locate the blockage.
Placing the Stent
The surgeon will pass a small wire with metal mesh through the catheter.
While a second catheter that is attached to a small balloon is inflated and will follow the guide wire.
Once the balloon catheter reaches the blocked artery of the patient, the doctor will inflate it.
This will force the artery to open and allow blood flow to return.
Then the doctor will insert the stent at the same time as the balloon angioplasty and it expands with the balloon.
Once the stent is secure, the surgeon will remove the catheter and make sure that the stent is in place.
However, some stents are drug-eluting stents, coated in medicine that slowly releases into the artery of the patient.
This will help keep the artery smooth and open and it helps to prevent blood flow to the heart and future blockages.
Closing the Incision
Following the stent placement, the doctor will close the incision and dress it, and then they will take the patient to the recovery room for observations.
A nurse will monitor the blood pressure and heart rate, while the patient will have limited movement during this time.
Most angioplasties with stent placements will need an overnight visit to make sure that there are no problems.
However, some people are allowed to go hon ome the same day.
After the Procedure
After the procedure, the incision site will be sore and possibly busied for a few days, and the movement of the patient will be limited.
However, your doctor will encourage short walks on flat surfaces.
The patient should make sure to avoid going up and down stairs or walking long distances in the first two to three days after the procedure.
Moreover, the patient will also need to avoid activities like driving, yard work, or sports.
The doctor will let the patient know when they can return to normal activities.
Also, the patient should make sure to always follow whatever instructions the doctor or surgeon gives, following the surgery.
Full recovery can take up to eight weeks from the procedure.

While the incision wounds heal, the doctor will advise the patient to keep the area clean to prevent any possible infection and change the dressing regularly.
Furthermore, the patient should contact the doctor immediately if they notice the following symptoms at the incision site:
- swelling
- redness
- discharge
- unusual pain
- bleeding that the patient is unable to stop with a small bandage.
On the other hand, the patient should also contact the doctor or surgeon immediately if they notice swelling in the legs, chest pain that does not go away, shortness of breath that does not go away, chills, a fever over 101°F, dizziness, fainting, extreme weakness,
Outlook and Prevention
While angioplasty with stent placement helps to address an individual blockage, it does not fix the underlying cause of the blockage.
In order to prevent further blockages, and reduce the risk of other medical conditions, the patient may have to make certain lifestyle changes.
These include eating a heart-healthy diet by limiting the intake of saturated fats, sodium, and processed foods, getting regular exercise, quitting smoking if they do because it can increase the risk of PAD, managing stress, and taking cholesterol-reducing medications in case the doctor prescribes them.
The patient should not perform any hard exercises or lift heavy weights after the procedure until the doctor says. it is often for at least 1 week.
However, they can walk around the house and do light activities while they should avoid bending, squatting, or climbing stairs for 24 hours after the procedure.
They should not wear tight or stiff clothing over the procedure site and will need to take a few days off from work and then return to work.
Moreover, the doctor will also recommend the long-term use of anticlotting drugs, like aspirin after the procedure. The patient should make sure to not stop taking these medications without talking to the doctor first.